Vitruvens Lab :
Innovation
& research
Energy management is becoming increasingly strategic for modern societies. The MedTech industry is no exception, with specific requirements related to device lifetime, patient experience, biocompatibility, and the balance between cost and patient benefit. VITRUVENS aims to play an active role in this evolution by driving advanced research activities to push existing energy limits and open new horizons for future medical devices.

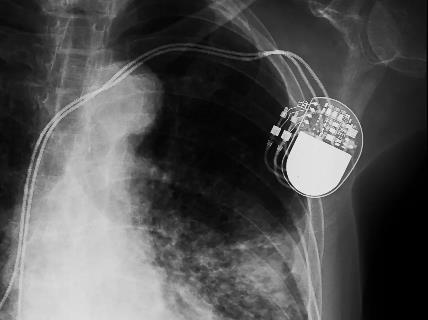
Xray picture of a pacemaker. Battery occupies more than half of the total volume
Active Implantable Medical Devices (AIMD)
Active Implantable Medical Devices (AIMDs) are electronic devices typically powered by non-rechargeable batteries. To ensure longterm operation, the battery must store sufficient energy, which often results in a bulky form factor, frequently occupying more than half of the total device volume, as illustrated by the X-ray image. Once the battery is depleted, surgical replacement of the entire device remains the only option. In some cases, the original device cannot be explanted, requiring a new device to be implanted alongside it. This leads to a poor patient experience, long-term biocompatibility challenges, and increased costs associated with repeated surgeries and device replacements. Furthermore, device longevity varies significantly between patients, depending on usage patterns and implantation quality.
From non rechargeable to rechargeable medical implants
To address these challenges, there is a growing shift toward rechargeable AIMDs. This transition enables a significant reduction in battery size, as the system only needs to store enough energy to power the device between recharging cycles. As a result, improved miniaturization is achieved and device lifespan is considerably extended without the need for additional surgery.

Transcutaneous Energy Transmission
Emerging Transcutaneous Energy Transmission (TET) systems now allow wireless recharging without percutaneous leads. While inductive charging is the standard—much like smartphone charging—it faces significant hurdles. These include risks of tissue overheating, short transmission ranges, and efficiency loss due to device misalignment.
Smart-UTET
SmartUTET™: The Future of Implant Powering
There is currently a proliferation of miniaturized implants, many of which are designed to be deeply embedded—up to 10cm—within the body. Early feedback from wireless charging technologies in medical applications suggests a need for higher misalignment tolerance. Consequently, conventional inductive Transcutaneous Energy Transfer (TET) no longer meets sufficiently the requirements of these new use cases
Redefining Transcutaneous Energy Transfer (TET) through Ultrasound Innovation.
To meet the demands of next-generation medical devices, Vitruvens introduces SmartUTET™ . Unlike traditional electromagnetic solutions, our technology leverages ultrasonic waves to deliver safe, deep, and reliable power to medical implants.
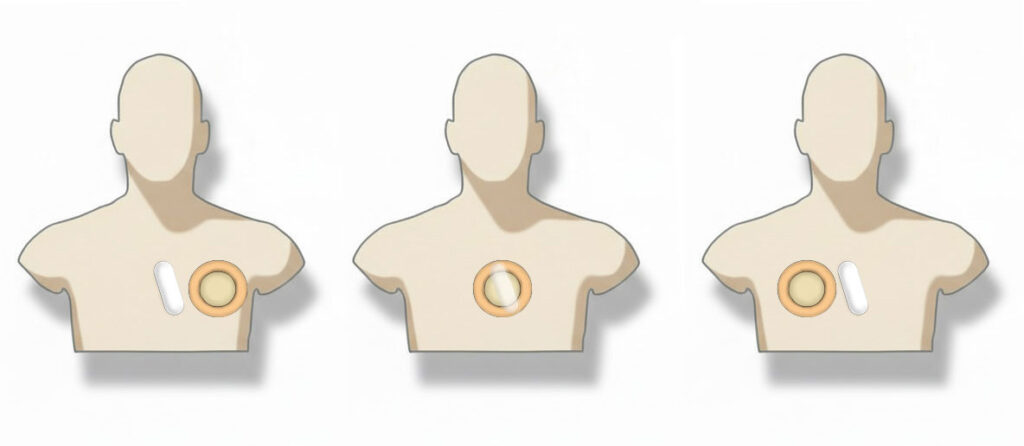
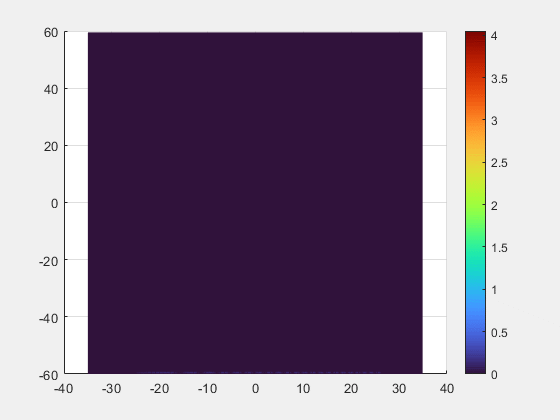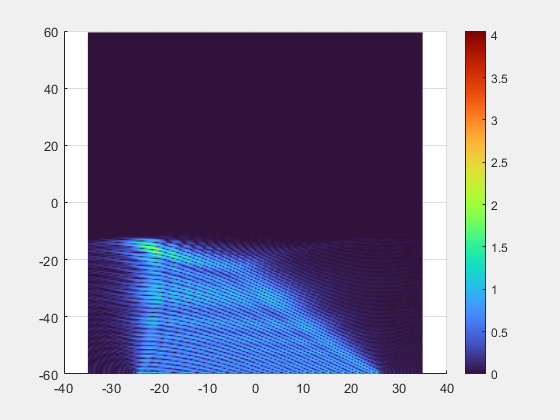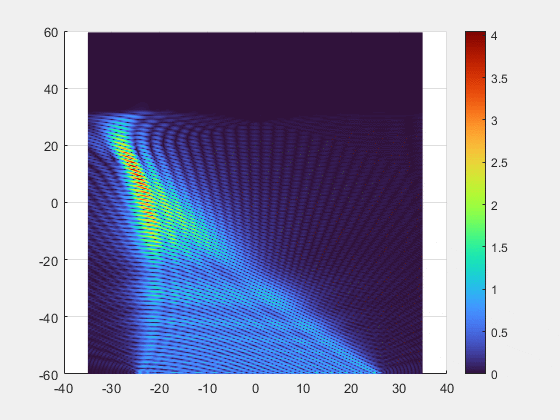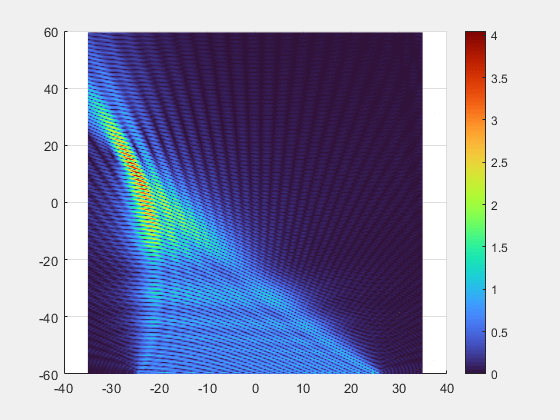
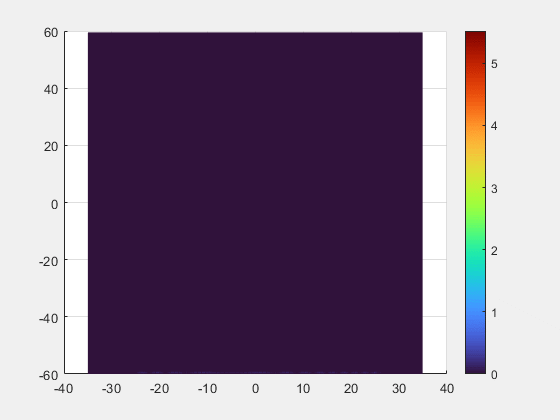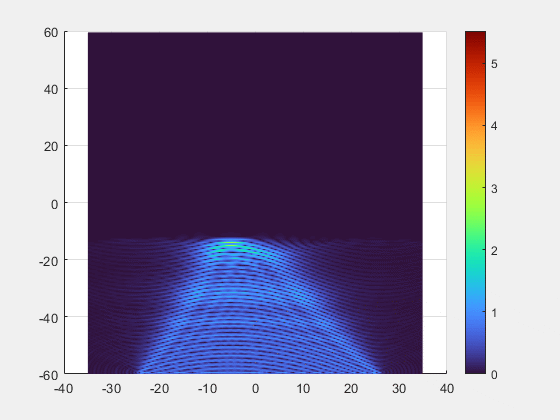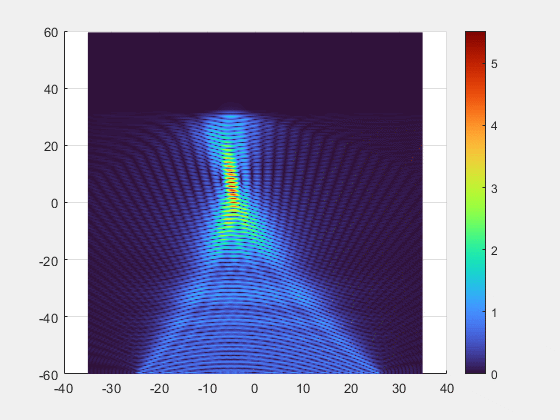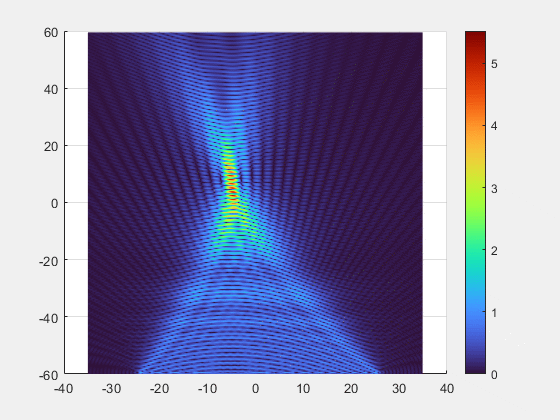
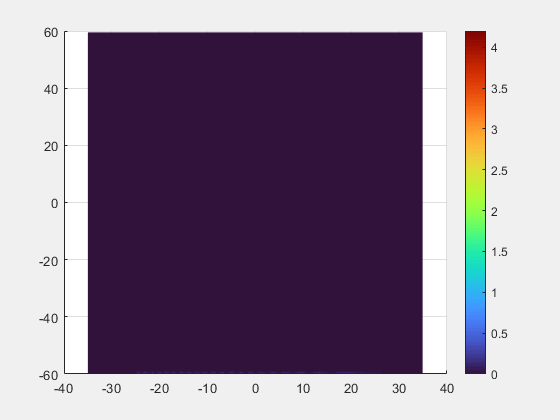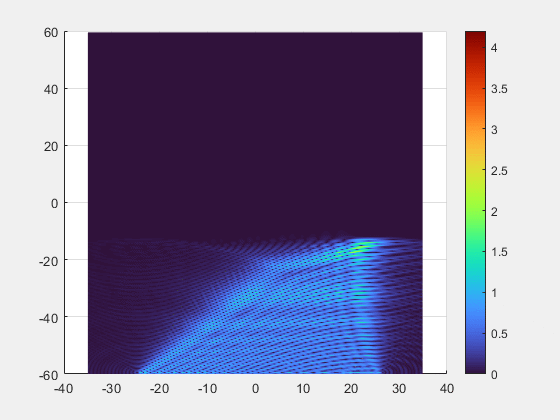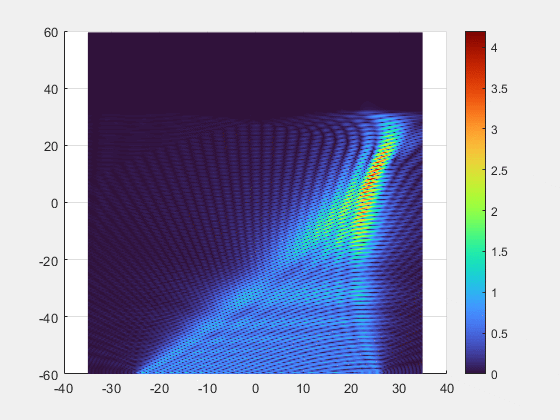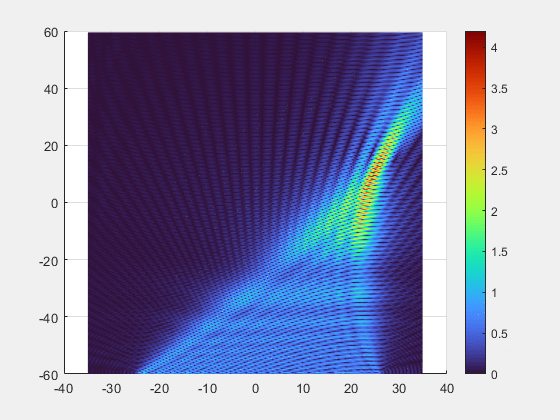
- Key Breakthroughs
- Adaptive Beamforming: Our multi-element transmitter automatically detects and tracks the implant, precisely focusing the energy beam where it is needed.
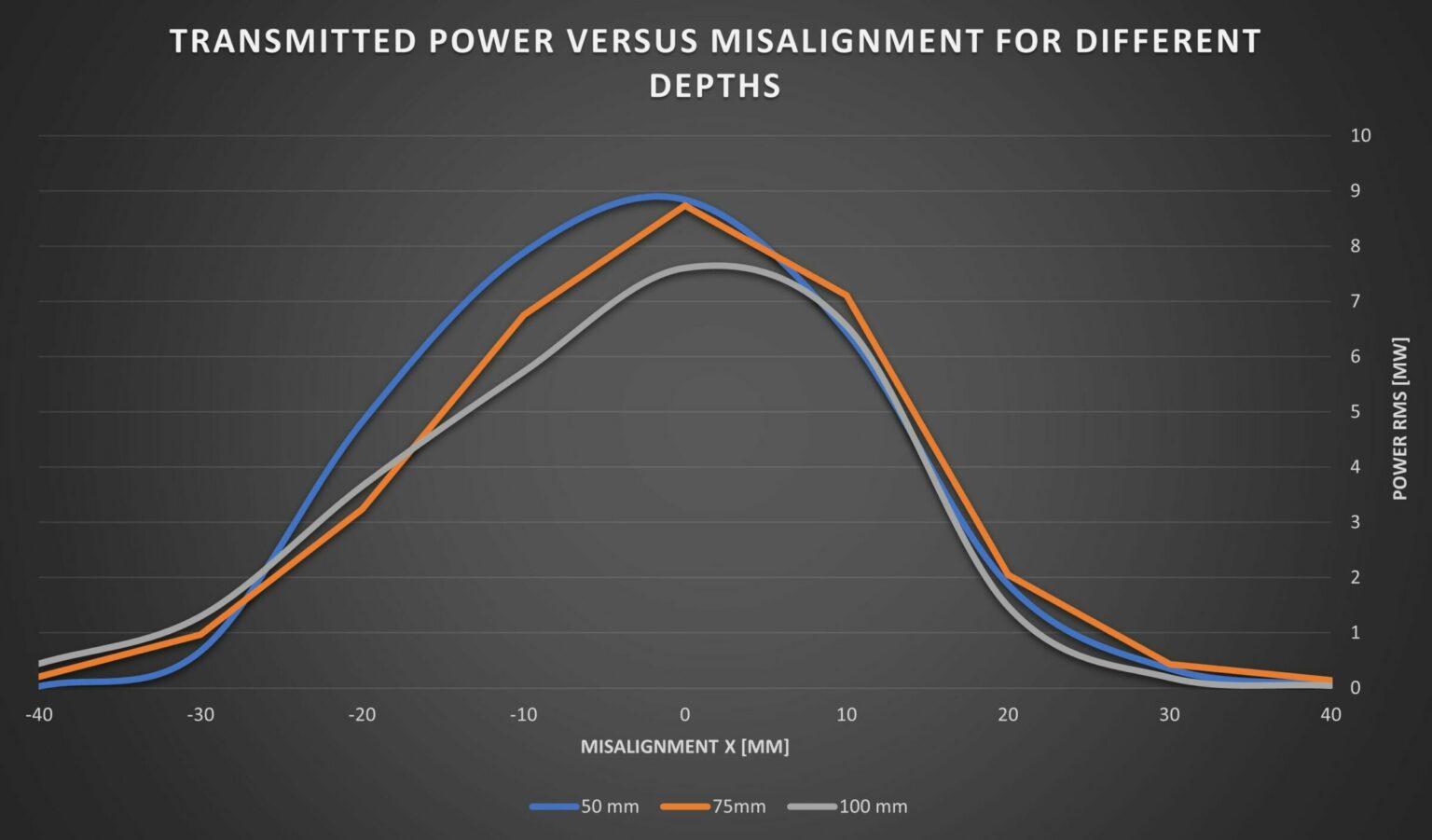
- Superior Alignment Tolerance: Unprecedented freedom of movement with axial misalignment tolerance of up to ±25 mm.
- Deep-Tissue Reach : Validated power transmission of 7 mW at 10 cm depth, enabling new possibilities for deeply implanted clinical applications.
- Titanium Compatibility : SmartUTET signals efficiently propagate through titanium housings, eliminating the need for complex “window” designs in implant enclosures.
- Integrated Data: Seamless combination of power delivery and high-fidelity data communication over the same ultrasonic signal.
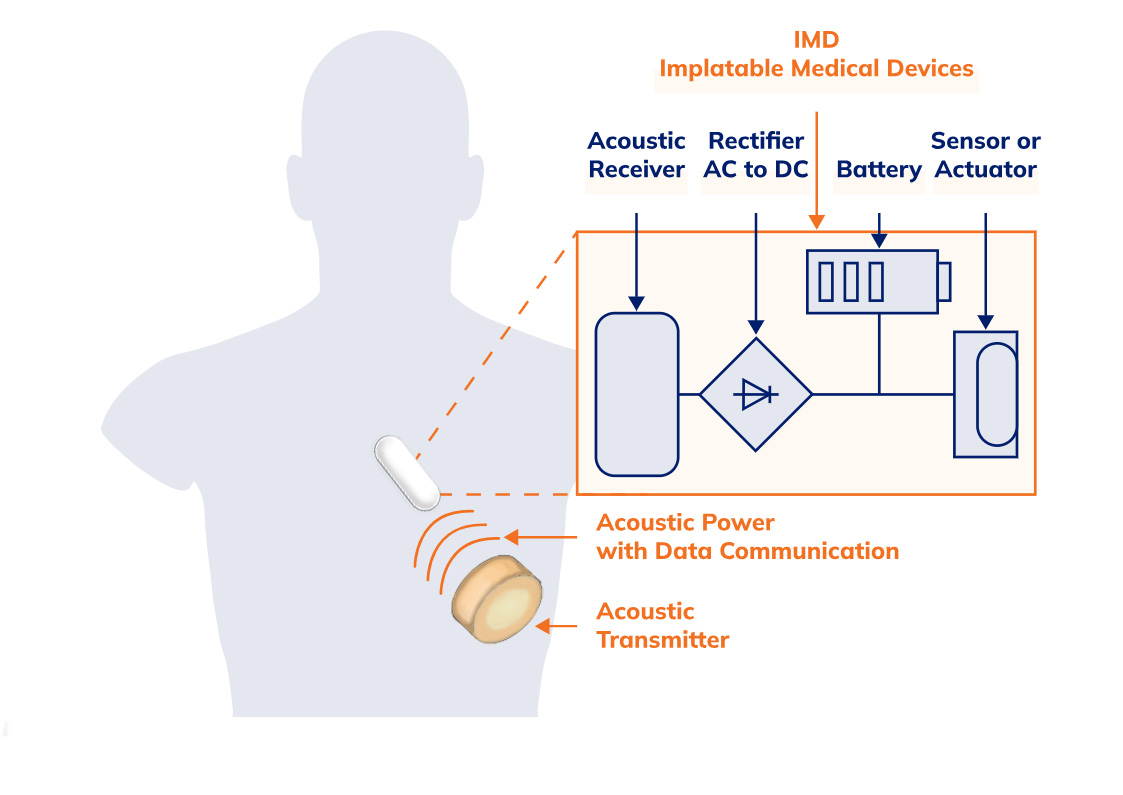
Understanding SmartUTET™ system: Ultrasonic energy transfer and communication
UER : is the sub part of SmartUTET™ integrated in the implantable device. The UER receives and converts the accoustic energy and the datas generated by the UET.
UET : is the external ultrasonic transmitter device. The UET generates an accoustic beam directed towards the UER. The UET transmits data to the UET over the the ultrasonic wave.
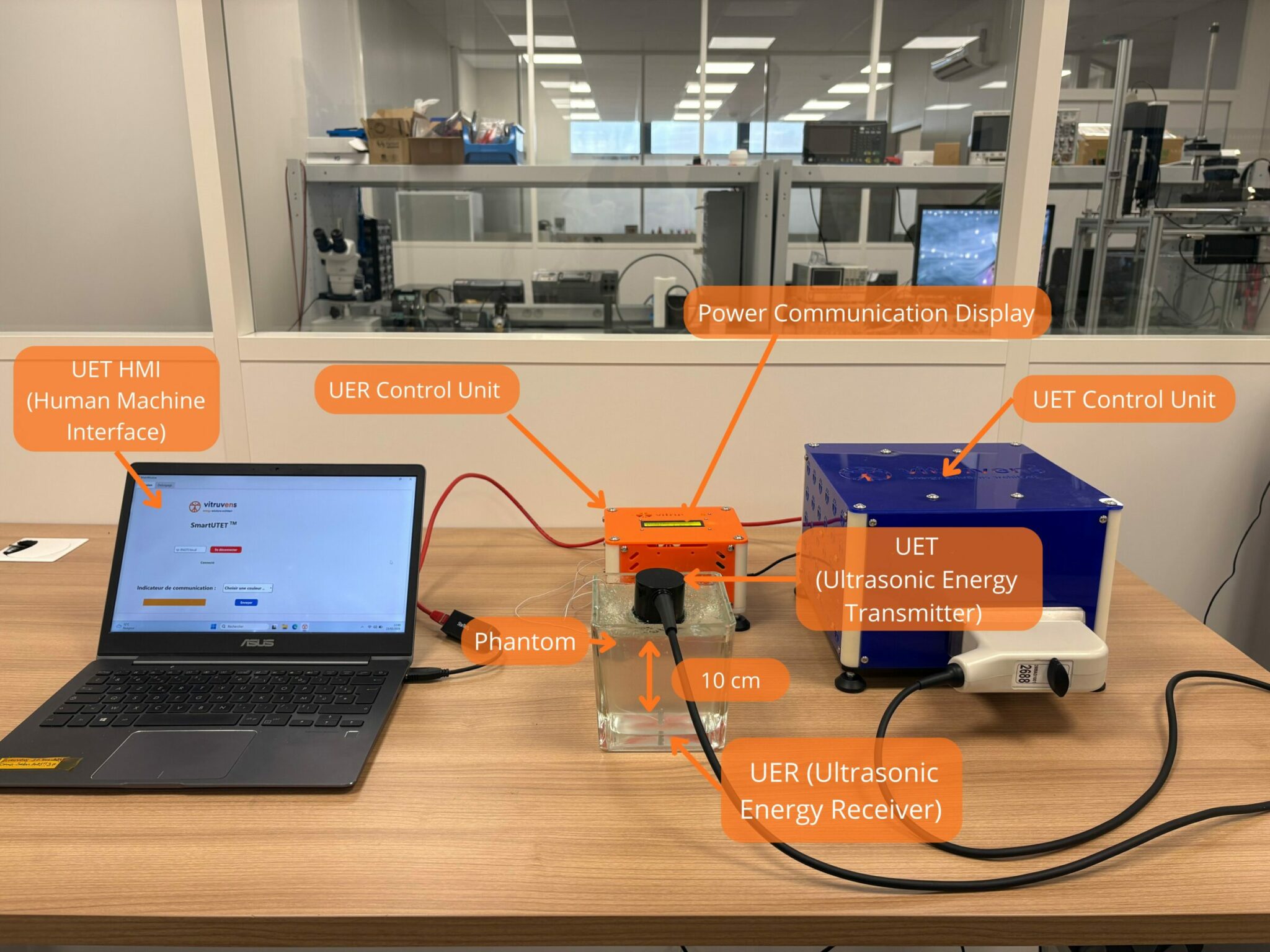
SmartUTET™ Demo is a non form factor demonstration system enabling to show the functionalities and the performances of SmartUTET™ technology
Power transmission and data communication animation
SmartUTET™ user experience example
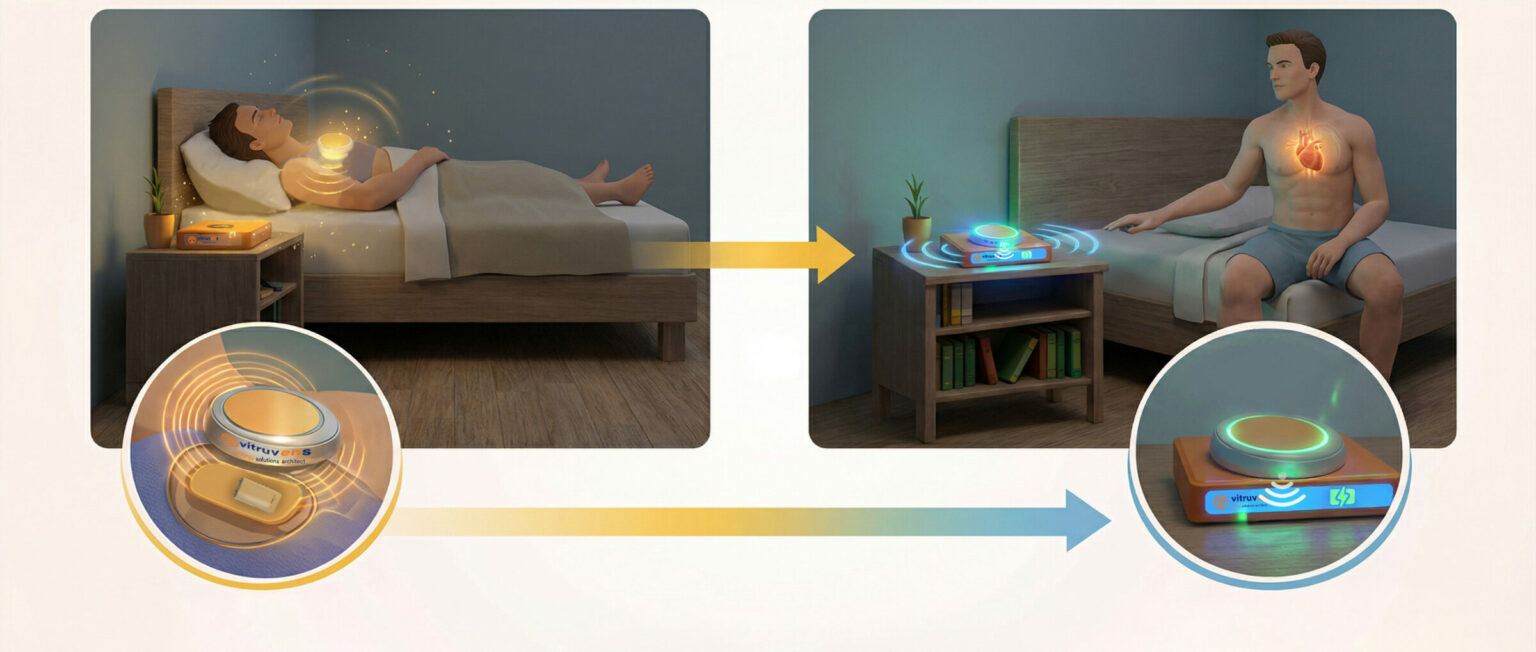

Implant recharge mode : acoustic transmitter worn by the patient. Implant recharge and data transfer.
Autonomous mode : acoustic transmitter placed in the docking station for recharging and data upload

Would your product benefit from one of these major innovations ?
Let us get in touch and explore how Vitruvens can take your device to next level

